
Scapular Pain? Here’s What You Need to Know
Scapular pain is something many of us deal with, but we often don’t pay much attention to it. This discomfort, which focuses around the shoulder blades, can be caused by things like muscle strain, bad posture, or even some underlying health problems.
Our scapula (shoulder blade) is super important for movement, stability, and good posture. When it gets irritated or overworked, it can cause sharp, dull, or burning pain that can get in the way of our everyday activities.
What is Scapular Pain?
Scapular pain refers to discomfort or pain felt around the scapula (shoulder blade), which is the triangular bone located on the upper back, between the ribs and the spine.
Scapular pain is often linked to poor posture, weak muscles, or injuries. (1)
Weakness in the scapular stabilizer muscles can lead to:
- Abnormal stress on the anterior shoulder capsule.
- Increased risk of rotator cuff compression (impingement).
- Reduced overall shoulder performance.
Common symptoms
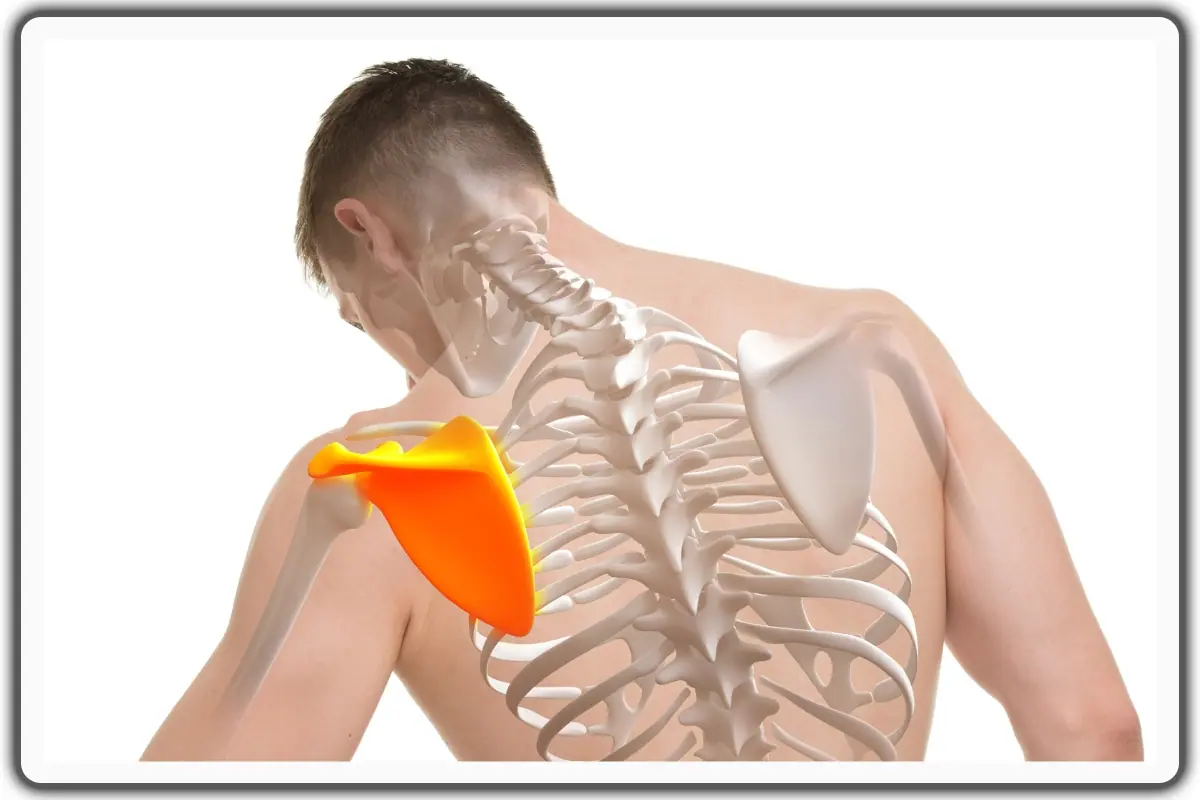
Pain or tenderness in the scapula area
Limited mobility or stiffness in the shoulder or upper back
Sharp or burning pain during overhead activities
Muscle strain or weakness in the shoulder or upper back muscles
Causes of Scapular Pain
Shoulder blade pain under your shoulder radiating to your back can be caused by various factors, including:
Snapping Scapula Syndrome: Disruption in scapula movement, often with overhead motions. (2)
Bursitis: Inflammation of the scapulothoracic bursa. (2)
Muscle Issues: Weak or overused scapular muscles leading to pain. (2)
Structural Issues: Abnormal scapula shape, tumors, or anatomical variations. (2)
Overuse or Repetitive Strain: Excessive activity causing irritation and muscle strain. (2)
Injury: Trauma or impact to the scapula area. (2)
Poor Shoulder Mechanics: Improper movement increasing strain on the scapula. (2)
Shoulder-related issues like shoulder impingement, rotator cuff injuries, or shoulder instability. (3)
Neck-related problems such as neck pain or nerve issues that affect shoulder movement. (3)
Posture-related issues, especially poor posture, which can change the resting position of the scapula. (3)
Importance of Stretching and Exercise
Targeted exercises and manual therapy to improve scapula movement and reduce pain. (1)
Gentle stretches can help to improve flexibility and reduce tension in the muscles of the scapula area.
Examples of gentle stretches include shoulder rolls, chest stretches, and upper back stretches.
Strengthening exercises can help to improve posture and reduce strain on the muscles and joints in the scapula area.
Examples of strengthening exercises include shoulder blade squeezes, rowing exercises, and upper back strengthening exercises.
Strengthening Exercises for Scapula
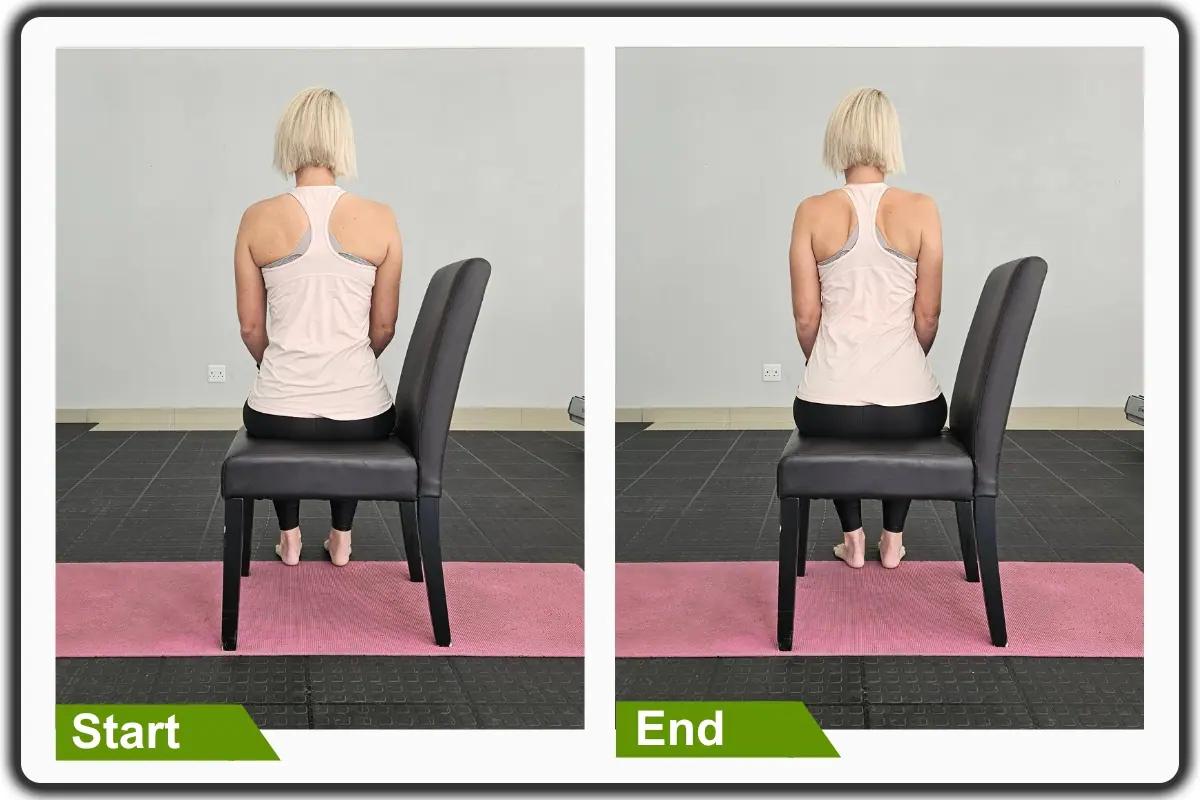
1- Scapular Squeezes
You can do this exercise in a seated or standing position.
Begin in an upright sitting position at the edge of the chair with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, and hips. Place your hands on your lap. Engage your core and gently pull your shoulders backward, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Hold the position for 5 seconds. Relax and repeat the movement. Complete 10 repetitions.

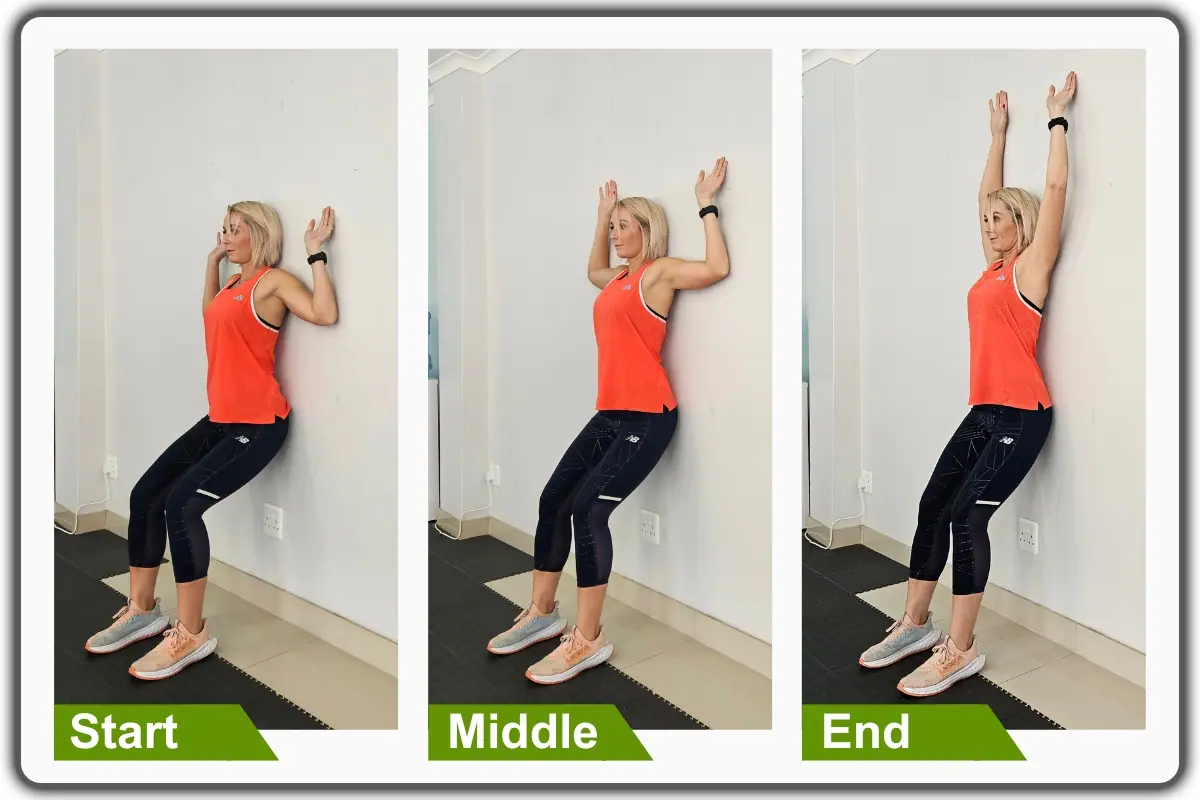
2- Wall Angels
Begin in an upright standing position in front of a wall with your feet shoulder-width apart, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs. Move closer to the wall and press your back against it. Engage your core. Slightly bend your knees as you bring your arms up to a “W” shape, with your elbows bent and hands near your head. Slowly slide your arms up to form a “Y” shape, keeping them as close to the wall as possible. Hold the position for a couple of seconds, then slide your arms back to the starting position. Repeat the sequence of movements with 10 repetitions.

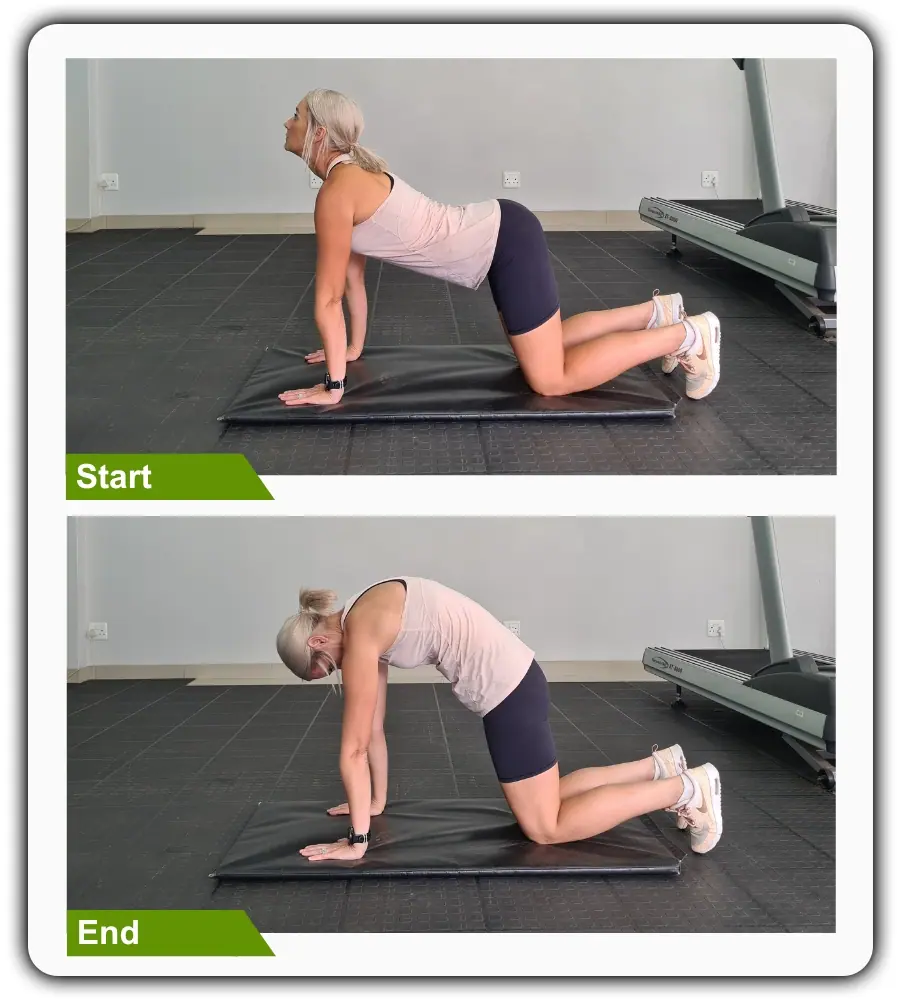
3- Cat-Cow Stretch
Begin in a 4-point position with your hands beneath your shoulders and your knees under your hips. Engage your core. Inhale as you arch your mid-back and lift your head upward. Then, exhale as you tuck your tailbone around your spine and lower your head downward. Repeat the sequence of movements with 10 repetitions.

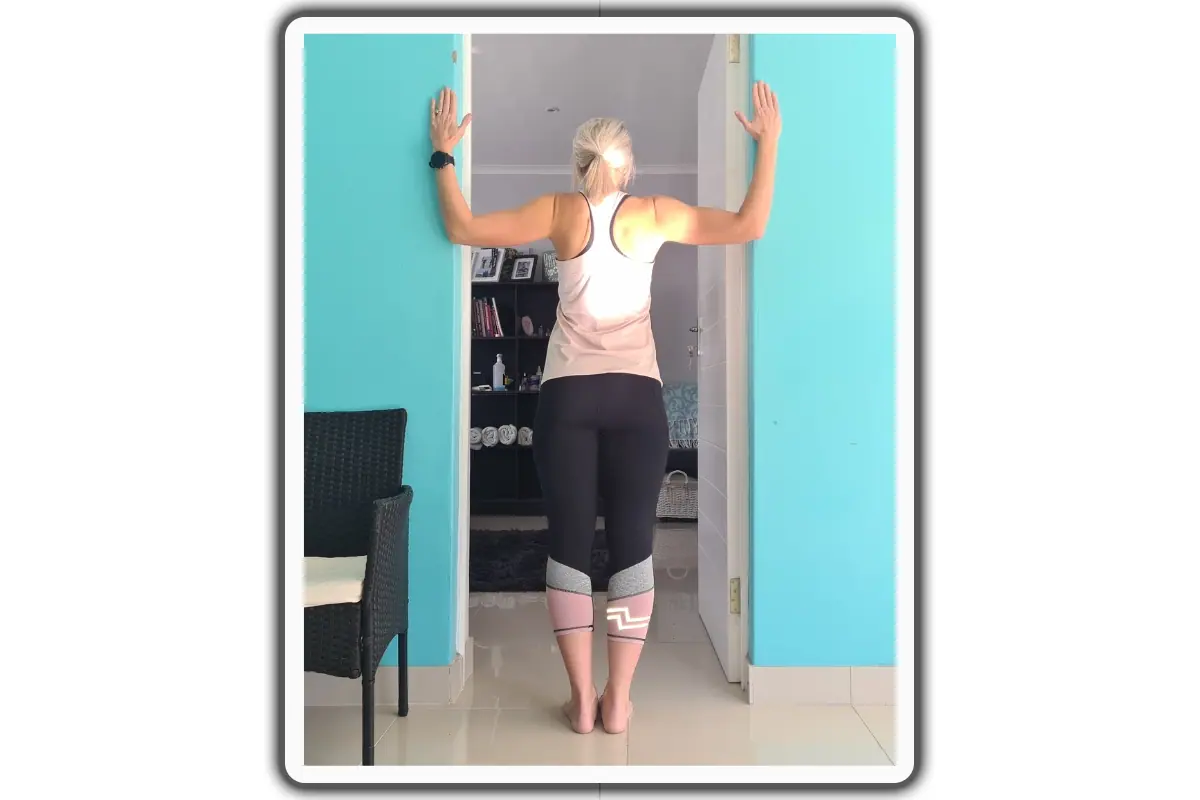
4- Pectoral Stretch
Begin in an upright standing position on a doorway with your feet hip-width apart, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs. Place your arms on the doorframe with your elbows bent at shoulder level. Engage your core. Step one foot forward and gently lean your body forward, squeezing your shoulder blades together and opening up your chest. Hold the position for several deep belly breaths, in through your nose and out through your mouth. Relax and repeat the movement with 5 repetitions.

Conclusion

Scapular pain can be a frustrating and limiting condition. While it often arises from common causes like poor posture and muscle strain, it's essential to recognize the potential for more serious underlying issues. By understanding the common symptoms, causes, and effective treatments, you can take steps to alleviate pain and improve your overall well-being.
Remember, if your scapula pain persists or worsens, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. By addressing the root cause of your pain and incorporating regular stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine, you can regain full mobility and enjoy a pain-free life.
Frequently Asked Questions:

What does it mean when your back hurts?
According to Dr. Anet Varghese, A common cause of back pain is injury to a muscle or ligament. These strains and sprains can occur for many reasons, including improper lifting, poor posture and lack of regular exercise, injury, overuse, arthritis, and other medical conditions, such as degenerative disk disease, being overweight, etc People who menstruate may also experience lower back pain related to their menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and conditions such as endometriosis.
Why does the back of my scapula hurt?
Pain in the back of the scapula can occur due to muscle strain, poor posture, or overuse of the muscles around the shoulder blade. Other possible causes include issues like scapular dyskinesis (abnormal movement of the scapula), pinched nerves, or referred pain from the neck or upper back. If the pain is persistent or severe, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation.
When should I worry about scapular pain?
You should be concerned about scapular pain if:
It lasts for more than a few weeks despite rest or home care.
The pain is severe, sharp, or accompanied by swelling.
You experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in your arm or hand.
The pain interferes with your daily activities or sleep.
Seeking medical advice in these cases can help identify any underlying issues.
What is a red flag for upper back pain?
Red flags for upper back pain include:
- Sudden, severe pain that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Pain accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness.
- Fever, unexplained weight loss, or fatigue.
- Persistent pain after a fall, injury, or trauma.
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of strength in the arms or legs.
If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor immediately for further evaluation.
KW for references:
(1) Scapula back pain - https://www.jmptonline.org/article/S0161-4754(06)00311-3/fulltext
(2) Causes of Scapula Pain - https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2008.12.022
(3) Shoulder-related issues - https://doi.org/10.1051/sicotj/2019029
References:
(1) Nijs, J., Roussel, N., Struyf, F., Mottram, S., & Meeusen, R. (2007). Clinical assessment of scapular positioning in patients with shoulder pain: State of the art. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics, 30(1), 69–75. https://www.jmptonline.org/article/S0161-4754(06)00311-3/fulltext
(2) Kuhne, M., Boniquit, N., Ghodadra, N., Romeo, A. A., & Provencher, M. T. (2009). The snapping scapula: Diagnosis and treatment. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery, 25(11), 1298–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2008.12.022
(3) Panagiotopoulos, A. C., & Crowther, I. M. (2019). Scapular dyskinesia, the forgotten culprit of shoulder pain and how to rehabilitate. SICOT Journal, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.1051/sicotj/2019029
